How Do Peanuts Grow? Unearthing the Fascinating Process
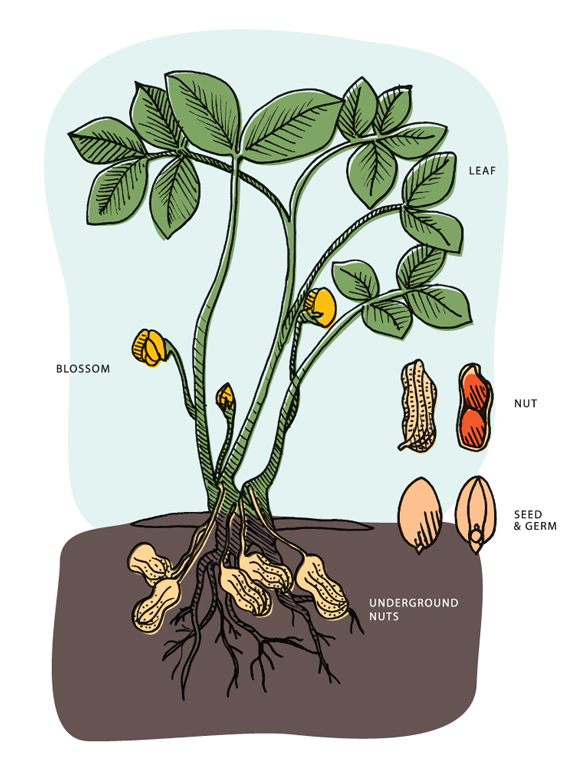
Peanuts grow underground as the seeds of the peanut plant. The plant produces yellow flowers that bend down and bury themselves in the soil, where the peanuts develop and mature.
Peanuts, scientifically known as Arachis hypogaea, are a fascinating crop that has been cultivated for thousands of years. These legumes are unique in the way they grow, with their seeds developing underground. In this blog post, we will explore the life cycle of peanuts, from planting to harvesting, and uncover the secrets behind their growth.
Understanding how peanuts grow can provide insights into the agricultural practices involved in their cultivation and the nutritional benefits they offer. So, let’s dive into the world of peanuts and discover the wonders that lie beneath the surface.
The Lifecycle Of A Peanut Plant
Peanuts begin as seeds planted in the soil. The plant blossoms, forming yellow flowers that eventually develop into pods underground. The pods mature, and the peanuts grow inside, ready for harvesting when the plant wilts.
Peanuts are a fascinating crop to grow, and they have a unique lifecycle that is unlike any other plant. Understanding the stages of a peanut plant’s lifecycle can help you grow your own peanut plants successfully. In this article, we will take a closer look at the lifecycle of a peanut plant, focusing on the subheading: From Seed to Sprout and Flowering and Pegging.
From Seed To Sprout
Peanuts begin their lives as seeds, which are planted in the soil. The seeds require warm soil temperatures to germinate, and they will begin to sprout after a week or two. Once the seed has sprouted, a taproot grows down into the soil, while a shoot grows upwards towards the surface. The shoot will eventually break through the soil’s surface, and the plant will begin to grow leaves. As the plant continues to grow, it will develop small, yellow flowers that are essential for peanut production.
Flowering And Pegging
Once the peanut plant has grown leaves, it will begin to flower. The flowers are self-pollinating, and they will develop into a structure known as a peg. The peg grows down towards the soil, and once it reaches the ground, it will penetrate the soil and begin to develop into a peanut. As the peanut develops, it will require plenty of water and nutrients from the soil. It is essential to keep the soil consistently moist during this stage of growth to ensure that the peanuts develop correctly. In conclusion, the lifecycle of a peanut plant is a fascinating process that requires specific conditions and care to ensure successful growth. By understanding the stages of growth, you can grow your own peanut plants and enjoy a bountiful harvest of delicious peanuts.
Peanut Varieties And Their Unique Characteristics
Runner Peanuts
Runner peanuts are known for their high yield and resistance to diseases.
Virginia Peanuts
Virginia peanuts are large in size and are often used for gourmet snacks.
Spanish Peanuts
Spanish peanuts have a small size and are used primarily for peanut candies.
Valencia Peanuts
Valencia peanuts are sweet in flavor and are commonly used for peanut butter.
Cultivation Techniques For Optimal Growth
To achieve optimal growth for peanuts, proper cultivation techniques are crucial. Peanuts grow best in well-drained sandy soil and require warm temperatures for successful development. Adequate spacing, regular watering, and sufficient sunlight are key factors for maximizing peanut yield.
Cultivation Techniques for Optimal Growth Peanuts are a staple crop in many parts of the world and are used in a variety of ways, from peanut butter to roasted snacks. For optimal growth, it is essential to follow proper cultivation techniques. In this section, we will explore the various methods for cultivating peanuts, including soil preparation, planting strategies, and watering requirements. Soil Preparation Before planting peanuts, it is crucial to prepare the soil adequately. Peanuts grow best in well-draining, sandy soil that is rich in organic matter. The soil should be free of weeds and any debris that may impede root growth. You can use a soil test kit to determine the pH level of the soil, which should ideally be between 5.5 and 6.5 for optimal peanut growth. Planting Strategies Peanuts grow best in warm weather, and planting should be done after the last frost has passed. The seeds should be planted about 2-3 inches deep, with a spacing of about 6-8 inches between each seed. It is essential to ensure that the soil remains moist during the germination period, which typically lasts between 7-10 days. Watering Requirements Peanuts require consistent watering throughout their growth cycle. It is recommended to water them deeply once a week, ensuring that the soil remains moist but not waterlogged. Overwatering can lead to root rot and other fungal diseases, so it is essential to monitor the moisture levels closely. In conclusion, following proper cultivation techniques is crucial for optimal peanut growth. By preparing the soil adequately, planting the seeds correctly, and providing consistent watering, you can ensure a healthy and bountiful peanut harvest.
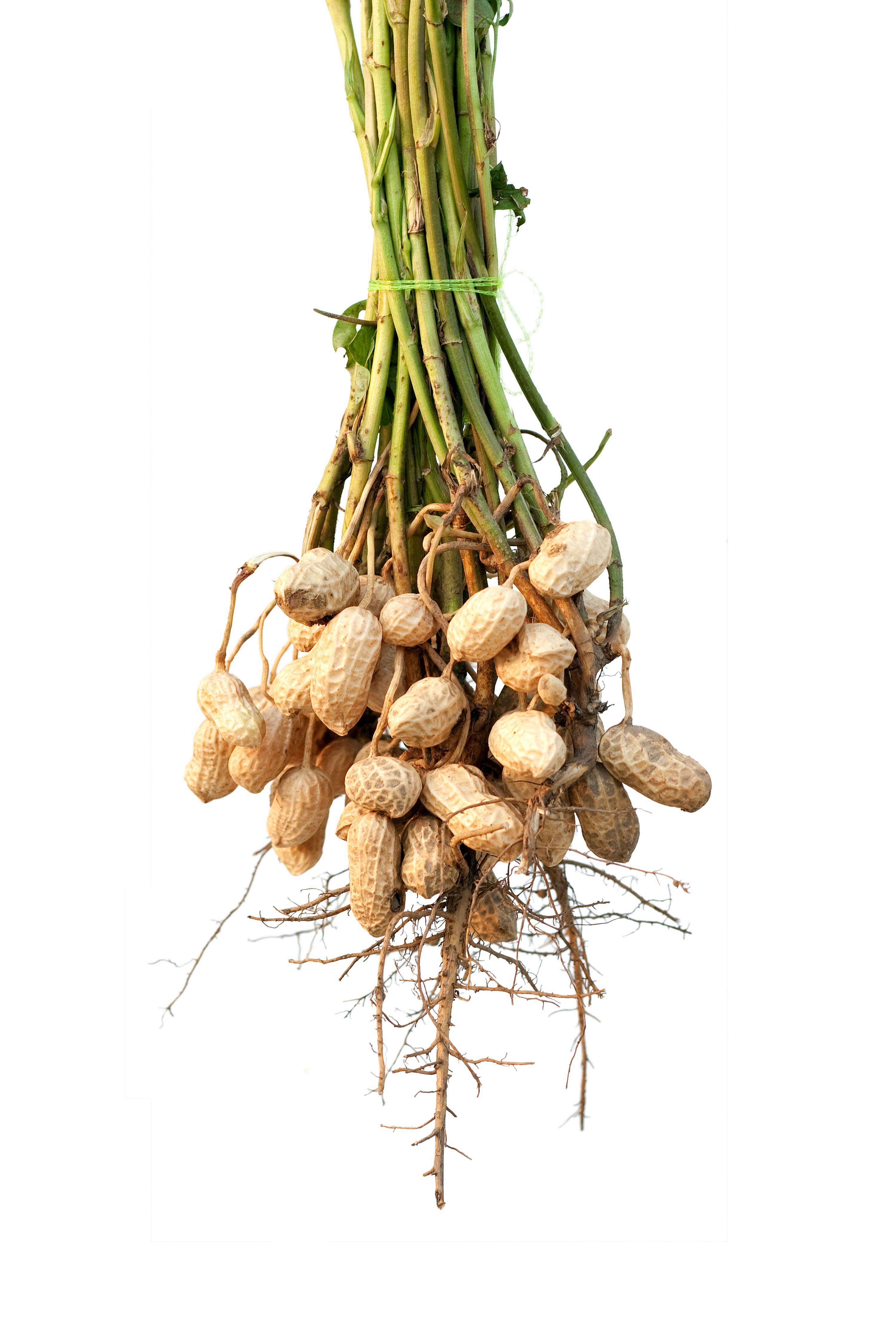

Credit: www.countryliving.com
The Underground Development
Peanuts, an underground development, grow from seeds planted in loose soil. The process involves flowering, pollination, and the formation of peanut pods underground, providing the perfect conditions for their growth.
Peanuts, known for their delicious taste and crunchy texture, have a fascinating underground development process. This process involves the formation of peanuts below the surface of the soil. Understanding how peanuts grow underground can give us a deeper appreciation for this popular legume.
How Peanuts Form Below The Surface
Peanuts undergo a unique development process that takes place underground. It all begins with the planting of peanut seeds in the soil. Once planted, the seeds germinate, and a small plant emerges from the ground. This plant then begins to grow both upwards and downwards, with its roots extending deep into the soil while the stem and leaves grow above ground. As the peanut plant continues to develop, it forms yellow flowers that eventually wither away. What remains after the flowers fade are elongated structures called pegs. These pegs, or stalks, start to bend downwards and penetrate the soil. It is through this downward growth that the peanuts begin to form. The pegs continue to grow and elongate, eventually reaching a depth of several inches below the soil’s surface. Once underground, the pegs form protective coverings around the developing peanuts. These coverings act as a shield, safeguarding the peanuts from external factors such as harsh weather conditions and pests. Inside these protective coverings, the peanuts undergo further growth and maturation. Over time, they develop into the familiar oval-shaped legumes we know and love. Once fully matured, the peanuts are ready to be harvested and enjoyed as a tasty snack or used in various culinary creations.
The Role Of Soil In Peanut Development
The soil plays a vital role in the development of peanuts underground. Peanuts require well-drained soil with good moisture retention capabilities. This type of soil provides the necessary environment for optimal growth and development. The soil’s moisture content is especially crucial during the early stages of peanut development. Adequate moisture allows the pegs to penetrate the soil easily and establish a firm connection with the ground. It also ensures that the peanuts receive sufficient water for their growth and development. Additionally, the soil’s composition and nutrient content directly impact the quality and yield of peanuts. Peanuts thrive in soil that is rich in organic matter and nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. These nutrients are essential for the plant’s overall health and the production of high-quality peanuts. In conclusion, the underground development of peanuts is a fascinating process that involves the formation of peanuts below the surface of the soil. Understanding how peanuts grow and develop underground gives us a deeper appreciation for these versatile legumes. The role of soil, moisture, and nutrients in peanut development cannot be underestimated, as they directly contribute to the quality and yield of this beloved crop. So, the next time you enjoy a handful of peanuts, take a moment to appreciate the remarkable journey they underwent beneath the soil.
The Harvesting Process
The Harvesting Process is a crucial stage in the growth and production of peanuts. It requires precision, timing, and proper equipment to ensure a successful harvest. Let’s explore the key aspects of the harvesting process, from determining the right time to harvest to the equipment and methods involved.
Determining The Right Time To Harvest
Peanuts are typically ready for harvest about 120 to 150 days after planting. The key indicator of readiness is the yellowing of the leaves, signaling that the peanuts are mature and ready to be harvested. Farmers also conduct a pod maturity test by digging up a few peanuts to check if the kernels inside have reached full size and are mature enough for harvesting.
Harvesting Equipment And Methods
When it comes to harvesting peanuts, farmers utilize specialized equipment such as a digger or shaker to loosen the soil and lift the plants from the ground. The peanuts are then left to dry for a few days before being collected using a combine harvester, which separates the peanuts from the vines and places them in a hopper for further processing.
Credit: www.flpeanuts.com
Post-harvest Handling And Storage
Peanuts grow underground and are harvested by pulling up the entire plant. After harvesting, the peanuts are dried to reduce moisture content and prevent mold growth. Once dried, they are stored in well-ventilated containers to maintain quality and prevent spoilage.
Proper post-harvest handling and storage are crucial for preserving the flavor and nutritional value of peanuts.
Drying Peanuts
After harvesting peanuts, the next crucial step in post-harvest handling is drying. Proper drying ensures that the peanuts retain their quality and prevent the growth of molds or fungi. It is essential to dry peanuts thoroughly before storing them to prevent spoilage. Drying peanuts involves removing the excess moisture from the kernels. This can be done through natural sun-drying or using mechanical dryers. Sun-drying is a traditional method where the peanuts are spread out in a thin layer on clean, dry surfaces and exposed to direct sunlight. Mechanical dryers, on the other hand, utilize hot air to accelerate the drying process. Regardless of the drying method used, it is important to monitor the moisture content of the peanuts regularly. The ideal moisture content for dried peanuts is around 8-10%. This ensures that the peanuts are properly dried and ready for storage.
Storing For Freshness
Once the peanuts are dried, proper storage is crucial to maintain their freshness and quality. Storing peanuts in appropriate conditions helps extend their shelf life and preserve their taste and texture. Here are some important factors to consider when storing peanuts: 1. Temperature: Peanuts should be stored in a cool and dry environment. Ideally, the temperature should be between 60-70°F (15-21°C). Avoid storing peanuts in areas that are prone to high temperatures or humidity, as this can lead to spoilage. 2. Packaging: Peanuts should be stored in airtight containers or bags to prevent moisture and pests from entering. This helps maintain their freshness and prevents contamination. 3. Avoid exposure to sunlight: Direct sunlight can cause the peanuts to spoil quickly and lose their flavor. Store peanuts in a dark area or in opaque containers to protect them from sunlight. 4. Proper ventilation: Ensure that the storage area has good air circulation to prevent the buildup of moisture. This helps prevent the growth of mold or fungi. 5. Rotation: When storing peanuts, it is important to follow the “first in, first out” rule. Use the older stock first to ensure that peanuts are consumed before their quality deteriorates. By following these guidelines for post-harvest handling and storage, you can ensure that your peanuts remain fresh and of high quality for an extended period. Proper drying and storage techniques play a vital role in preserving the flavor and nutritional value of peanuts, making them enjoyable for consumption or use in various culinary applications.
Peanuts And Their Nutritional Profile
Peanuts are not actually nuts but legumes that grow underground. Let’s explore the nutritional profile of peanuts and discover the health benefits they offer.
Health Benefits Of Peanuts
Peanuts are rich in protein, healthy fats, and antioxidants.
Nutrient Content
Peanuts are packed with vitamins, minerals, and fiber.

Credit: www.thetreecenter.com
Peanuts In Cuisine And Industry
Peanuts grow underground and are a type of legume. They are an important crop in many parts of the world, used in both cuisine and industry. Peanuts are grown in warm climates and need well-drained soil to thrive.
Culinary Uses
Peanuts are versatile ingredients in various cuisines worldwide. They are commonly used in savory dishes and desserts. Peanut butter is a popular spread made from roasted peanuts.
Non-food Products
Peanuts have diverse applications beyond food consumption. They are utilized in the production of cosmetics and soaps. Peanut shells are used for mulch and fuel.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Peanuts Grow?
Peanuts grow underground, not on trees. The plant flowers above ground but then the peanut pods develop beneath the soil. The peanut plant requires warm weather and plenty of moisture to thrive.
What Is The Growing Period For Peanuts?
Peanuts typically take 4-5 months to reach maturity. They are planted in the spring and harvested in the fall. The growing period includes flowering, peg penetration into the soil, and pod development.
What Kind Of Soil Do Peanuts Need?
Peanuts thrive in well-drained sandy loam soil. They require soil with a pH level between 5. 8 and 6. 2. The ideal soil allows for easy penetration of the pegs, which are small stems that grow downward from the flowers to penetrate the soil and develop the peanut pods.
How Are Peanuts Harvested?
Peanuts are harvested using specialized equipment that digs the plant out of the ground. The plants are then inverted and left to dry in the field for a few days. After drying, the peanuts are picked up, threshed, and cleaned.
Conclusion
Understanding how peanuts grow can deepen appreciation for this popular legume. From planting to harvesting, the growth process is fascinating and intricate. By recognizing the conditions and care needed, farmers and gardeners can ensure a successful peanut crop. Learning about peanut growth enhances our connection to the food we consume.

